|
Income and cross elasticity of demand |
Income elasticity of demand |
|
Income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of demand to changes in income:
|
|
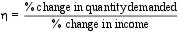
|
|
Demand and income |
|
Demand for a good will usually be affected by the income of the people buying it. One would assume that the demand for a good will increase as income of consumers increases. However, this is not always the case, so it is important to distinguish those cases when the demand does increase from those when the demand does not increase.
|
|
|
A normal good is one when an increase in income leads to an increase in demand. However, an inferior good is one where an increase in income leads to a fall in demand.
|
|
|
Examples of inferior goods are (a) bread (b) public transport.
|
|
Cross elasticity, pricing policy and competition
|
| The demand for one good can influence the demand for another. Two goods may be either complements or substitues. |
|
Complements
|
|
|
|
|
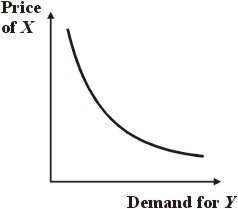
For complementary goods, X and Y, when the price of X goes up, the demand for Y goes down.
|
|
|
Substitutes
|
|
|
|
|
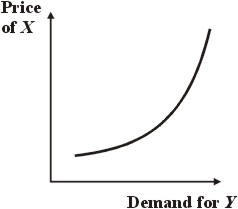
For substitutes, X and Y, an increase in the price of X causes an increase in demand for Y, as consumers switch from X to the substitute good Y.
|
|
|
There can also be the equivalent concepts for supply: joint supply (for example, supply of beef and leather), and competitive supply (for example, supply of beef and lamb).
|
|
|
Demand can be influenced by other factors: (a) sociological and demographic; (b) psychological; (c) “Acts of God”; (d) rules and regulations.
|
|
|
Income also influences demand, which leads to the concepts of inferior and superior goods.
|
|
|
One kind of inferior good is called a griffen good. This is a good that can have a positively sloped demand curve. This occurs when the good is a staple good. Thus, when poor people are improverished by a rise in the price of a staple good, they must buy more of the staple good in order to survive.
|
|
|
Cross elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of demand of one good X to changes in the price of another good Y.
|
|
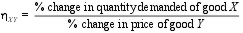
|
|
|